Donate Blood for Research
 MEDICAL BREAKTHROUGHS depend on research donations from people like you
MEDICAL BREAKTHROUGHS depend on research donations from people like you
 MEDICAL BREAKTHROUGHS depend on research donations from people like you
MEDICAL BREAKTHROUGHS depend on research donations from people like youWhen you join our donor research program and donate blood for research, you are contributing to scientific knowledge and medical breakthroughs that may help people with cancer, heart disease, and autoimmune diseases in the future. Hospitals, research institutions and biopharma companies rely on these donations for their ongoing medical research. Here is how you can contribute.
If you are not eligible to donate to the community blood supply, you can still help others by joining our donor research program! Because blood donated for research purposes will not be used to treat actual patients, more people are eligible to donate.
Maximize Your Impact: Types of Research Donations
There are 4 ways to donate blood for research with Bloodworks Northwest. You can donate whole blood, white blood cells, mobilized blood-forming cells, or participate in the All of Us Research Program. Explore the different types of donation opportunities available, then fill out My Donation Form linked below. A Bloodworks Bio team member will reach out to help you identify the most suitable type of donation for you.
Whole Blood
• Fastest donation (less than 30 minutes)
• Deferred community blood donors may be eligible
Learn More
What is it? Whole blood refers to the blood flowing through your arteries and veins – it contains white blood cells, red blood cells, platelets, and plasma. This is our quickest research donation, and can be helpful for many research studies.
The process: Blood is drawn from your arm into tubes, syringes, and/or sterile bags.
How much time does it take? Less than 30 minutes
What type of research could a whole blood donation support? These donations are used for many research purposes, including but not limited to research studies involving cancer, metabolic diseases, autoimmune diseases, and blood clotting disorders.
How often can I donate? Up to once per week with a maximum blood donation volume equivalent to one unit of blood every 56 days.

White Blood Cells
• Similar to a platelet apheresis donation
• Time to relax (with a warm blanket!)
• Deferred community blood donors may be eligible
Learn More
What is it? White blood cells are an important part of the immune system, protecting our body against infectious disease and foreign invaders. Scientists use white blood cells to study immune responses and for developing immunotherapies.
The process: Blood is drawn from your arm into a sterile machine that spins and separates the blood to remove just the white blood cells, returning the red cells, platelets, and plasma to your arm in a sterile manner. This process is called leukapheresis.
How much time does it take? 3-4 hours
What type of research could an apheresis donation support? These donations could be used for research studies involving cancer, metabolic diseases, and autoimmune diseases
How often can I donate? Up to once per week with a maximum of 12 times per year.

Mobilized Blood-Forming Cells
• Tremendous need for mobilized leukapheresis donations
• Most suitable for donors who are able to commit a significant amount of time
Learn More
What is it? All of our blood cells are made in the bone marrow by blood-forming cells. Mobilization medications are administered to a person to increase and/or release blood-forming cells from the bone marrow into circulating blood, which are then collected by leukapheresis.
The process: Donors will receive a series of mobilization medication(s) for several days prior to collection. On collection day, blood is drawn from your arm to a sterile machine that spins and separates the blood to remove just the white blood cells, returning the red cells, platelets, and plasma to your arm in a sterile manner. This process is called leukapheresis.
How much time does it take? Donors can expect a screening and blood draw appointment lasting up to 2 hours. Then, depending on the mobilization schedule, subsequent time commitments vary from 1-5 days of 30 minutes appointments to receive mobilization medications, followed by 1- 2 days of 4-6 hour leukapheresis donation appointments.
What type of research could a mobilized apheresis donation support? Mobilized apheresis donations can be used for research studies involving cancer, metabolic diseases, and autoimmune diseases
How often can I donate? Minimum of 6 months in between mobilizations.

All of Us Research Program
Bloodworks is excited to partner with the All of Us Research Program, a historic effort by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to engage 1 million participants from all across the United States.
+ Learn More
Am I Qualified to Donate Blood For Research? Find Out.
Blood Donation in 3 Easy Steps:
|
1. Screening
interview
|
2. Schedule an
appointment
|
3. Donate
|
Once qualified as a donor, you may be invited to donate multiple times.
Reimbursement is provided for your time and availability.
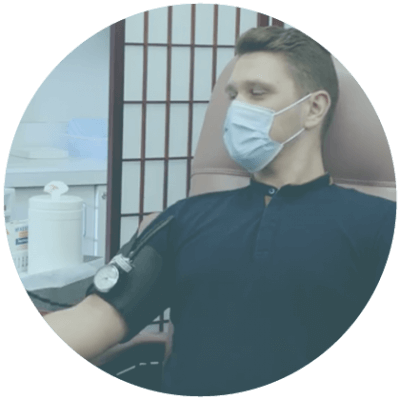
How Can I Prepare For my Blood Donation?
“It takes one moment of my day to potentially contribute to a medical breakthrough or a cure.”
ACCELERATING DISCOVERIES at the forefront of biomedical research by offering a complete ecosystem of blood-based biological products and cellular therapy support.
Executive Vice President
Aaron Posey



